- Blog
- EU Import Duties for Car Dealers and Traders
EU Import Duties for Car Dealers and Traders
Learn about EU import duties for car dealers, including VAT, registration tax, and excise duty. This overview of import duties will help you prepare yourself for the process of importing cars to Europe.

Trading cars within the EU is quite straightforward because there are rules and regulations for every step of the process. Stick to those, and you’re good!
However, the process is only easy if you have the correct information. We wanted you to know everything about the steps for paying import duties so you don’t run into any surprises, and that’s why we’ve gathered all the key details about importing a car from Europe.
So, let’s see what charges you’ll have to pay to stay compliant and owe nothing extra to the government.
Types of charges when importing vehicles in the EU
You’ll now see an overview of duties to pay when importing a car from Europe. Exact regulations and taxes vary from country to country, but we’ve compiled some common charges that you can expect.
Value Added Tax - VAT
In most cases, you’ll have to pay VAT in the country you’re importing your vehicles to. However, the precise amount to pay depends on several factors, such as:
- The country of registration
- Whether the vehicle is considered new or used
- Whether the seller is a private individual or a dealer
- The total price of the vehicle (including additional costs like delivery)
Since different scenarios are possible, you can visit the Your Europe website and go through an interactive guide to understand the specific VAT requirements for your situation.
Image source: Your Europe
The guide will take your answers and provide information about the VAT charges you may need to pay.
For instance, if you say that you’re buying a used car from a VAT-registered business within the EU, you’ll learn that the VAT may or may not be charged and mentioned separately on the invoice, depending on how the dealer opts to calculate VAT.
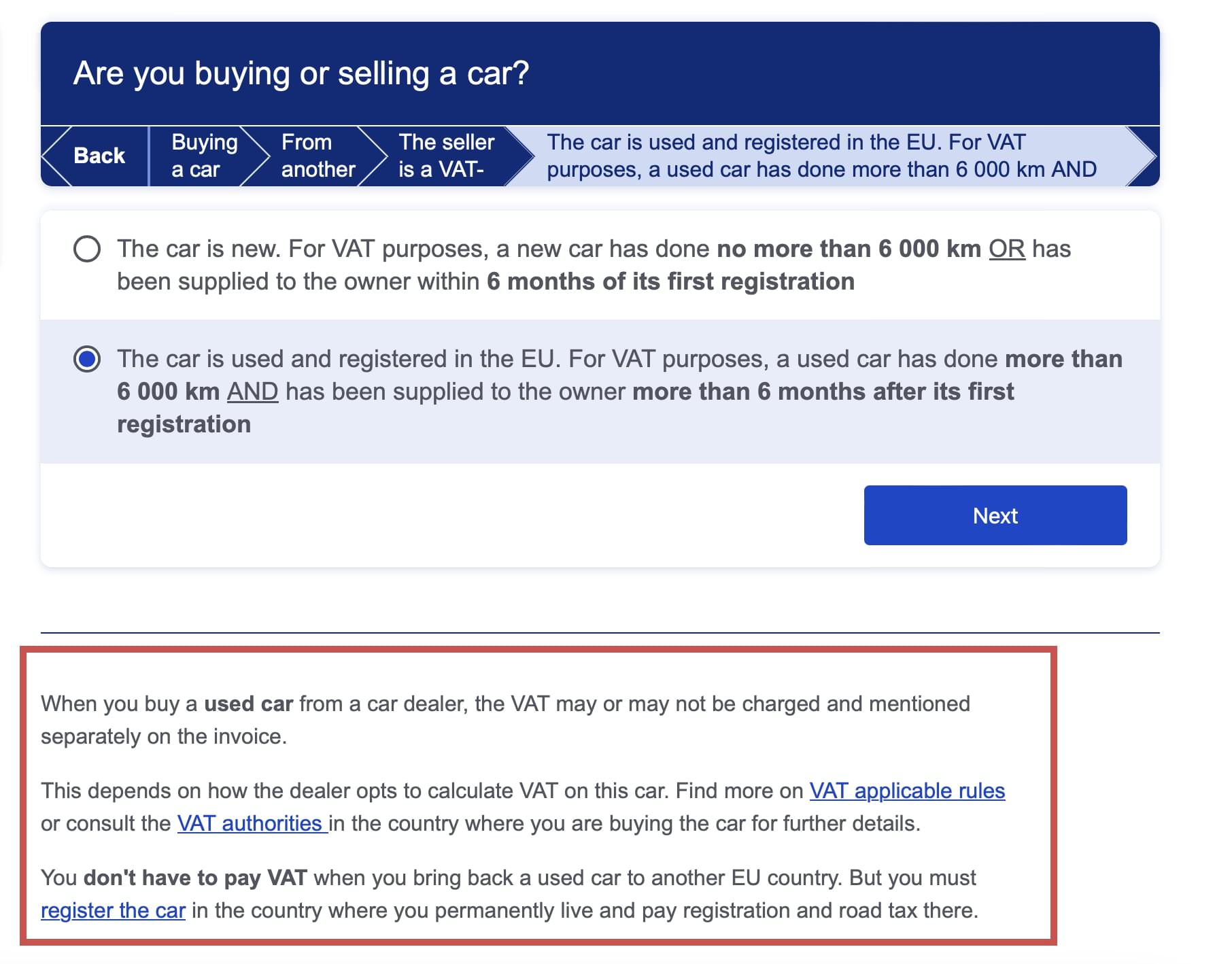
Image source: Your Europe
Most dealerships opt to sell vehicles VAT-excluded, so be prepared to pay VAT in your country of import.
Here’s the recap of what we’ve covered so far: Do you pay VAT on used cars?
Yes, you do, unless the VAT is included in the sale price.
The next question you probably have is how much VAT you’ll have to pay.
This depends on the standard VAT rate in your country of import.
The VAT rates are subject to change, so you should verify the current rates before buying. With that in mind, here’s a table with the current (July 2024) VAT rates for some EU countries:
|
Country of import |
VAT rate |
|
Belgium |
21% |
|
France |
20% |
|
Germany |
19% |
|
Italy |
22% |
|
Netherlands |
21% |
|
Poland |
23% |
|
Portugal |
23% |
|
Spain |
21% |
Now that the VAT is out of the way, let’s continue with the import duty.
Customs fees
Most EU members don’t charge customs fees for importing cars from other EU countries. That said, you should always check with your local customs or tax authorities, because there still may be some specific regulations that apply to your situation.
For instance, Portugal is one of the countries that charges a tax known as ISV (Imposto Sobre Veículos) even when importing within the EU.
ISV is based on the car’s engine size and CO2 emissions, and you’ll have to pay it even if you’re bringing the car in from another EU country.
If you’re importing from outside the EU, a 10% customs fee is usually applied to the car’s value.
Don’t forget that the car’s value includes not only the purchase price, but also extra costs like transport, insurance, and other expenses that come up before the car reaches the EU border.
To estimate the customs fees, simply calculate 10% of this total amount.
Registration Tax
Registration tax (also known as motor vehicle tax in some countries) refers to a one-time fee that you must pay when registering a vehicle in a new country. This tax is typically based on factors such as:
- Vehicle type
- The vehicle’s engine size
- CO2 emissions
- Age
- Value
The registration tax differs from country to country. Still, the amount you’ll have to pay doesn’t have to be a surprise because many EU member states offer online calculators that can help you estimate the tax you will need to pay.
Excise Duty
Just like VAT, the excise duty isn’t unique to vehicles. This duty is charged for specific goods, usually those that are considered harmful to public health or the environment.
For instance, excise duty is imposed on alcohol, tobacco, and fuel. In most EU members, it is not the vehicles themselves that are taxed with excise duty, but rather the fuel they use, as it contributes to environmental pollution through CO2 emissions and other pollutants.
You should bear in mind that the cost of excise duty is prone to changes. In fact, a report by Comite National Routier—an authority on road transport market analysis and research—shows some changes that are as recent as 2023.
Here’s the report's overview of vehicle excise duties.
|
Country of import |
Excise duties on diesel fuel for commercial use (in €/hl) |
Excise duties on diesel fuel for non-commercial use (in €/hl) |
|
Belgium |
39.51 |
60.02 |
|
France |
45.19 |
60.90 |
|
Germany |
47.04 |
47.04 |
|
Italy |
40.32 |
61.74 |
|
Netherlands |
41.75 |
41.75 |
|
Poland |
23.90 |
23.90 |
|
Portugal |
20.07 |
37.07 |
|
Spain |
33.00 |
37.90 |
Essentially, the more a vehicle pollutes, the higher the excise duty will be. That’s one of the reasons why many dealers are starting to include hybrids and EVs in their offer.
How to calculate import duties?
Most import duties are based on several factors, such as the vehicle’s engine size, CO2 emissions, and more.
Because these calculations include multiple variables, it may be more convenient to use online calculators than to estimate the duties by hand.
A Dutch vehicle tax approximation calculator
Even with calculators, you’ll need to do some preparation and gather information about your vehicle to ensure your calculations are as accurate as possible.
Here’s what you’ll need:
- Vehicle type
- Date of first registration
- Fuel type
- CO2 emissions
- The vehicle’s horsepower
- Engine size
- Purchase price
So, keep your certificate of conformity near, as the document contains plenty of helpful details you’ll need.
Bear in mind that most online calculators state that the calculation is approximate, so it’s better to contact the relevant authorities for precise information.
Also, remember to include all taxes that apply when importing a car from Europe. You should calculate the VAT, registration tax, excise duty, and any other local fees to get the complete cost.
Feeling overwhelmed? Don't worry, eCarsTrade is here to help
Taxes may seem confusing, but they shouldn’t be the obstacle that prevents you from importing quality cars from European countries.
For each tax or regulation, there’s a regulatory body that you can contact to inform you on the fees. And if you’d like to ensure you’ve taken absolutely every tax into consideration, it’ always a good idea to hire a specialized import agency.
So, if you decide to buy cars through eCarsTrade, you won’t be on your own—we’ll do our best to help you with advice and connect you with the experts so that you navigate the import process smoothly.
If you want to see what the process looks like, check out our case study on importing cars from Belgium to Portugal. We hope it gives you an idea of what you can expect when importing to your country!
Importing vehicles from Europe can be complex, but eCarsTrade is here to simplify the process. Learn how to: